The area of the foot between the base of the toes and the heel is called the arch. People require adequate arch formation and support to walk, run, stand and bear their body weight without pain. Let’s look at the kinds of arches and how to create and sustain healthy support for these important areas of the feet.
Types of Foot Arches
The arch is composed of tough tendons and ligaments which connect the bones and muscles of your feet, so they support your full body weight as you move efficiently and without discomfort. Most adults have what’s called a neutral, or medium, arch which is curved to support your body weight efficiently and adequately.
Other people, especially toddlers, have flat, or low, arches. This kind of foot structure provides less efficient movement and support. If you were to take an impression of a flat foot, you would see a complete footprint with no empty space between the heel and toes.
Finally, some people have high arches. Little of the footprint, except for the toes and part of the heel, shows upon gait analysis or casting when an arch is high. These arches are inefficient and often painful, particularly when the individual does strenuous activities, such as running.
Get the Arch Support You Need
This is where your foot and ankle doctor comes in. During an in-office exam, your podiatrist can tell you what kind of arch you have and what kind of support would help you avoid pain and fatigue in your lower extremities, have better balance and weight distribution and correct biomechanical problems. The doctor will take a painless three-dimensional scan of your foot to determine its structure and what you need to have the best foot function and comfort possible.
Wear Shoes Made of Quality Materials
Never wear cheap or worn-out shoes. Instead, select quality materials with adequate arch support and cushioning insoles. Lacing delivers support to the forefoot, too, and keeps your foot from shifting around inside your shoe. Make sure the shoes fit well in the heels to avoid wobbling.
Explore Custom-made Orthotics with Your Podiatrist
Crafted from high tech materials, these shoe inserts accommodate or correct problems with foot structure. Your foot and ankle doctor uses high-tech scans to produce orthotics suited to your particular foot health needs.
They are crafted for daily use in any and all kinds of footwear. Because they are designed by your foot doctor, these inserts are highly durable. They are considered very superior when compared to the many kinds of ready-made insoles available through retail outlets.
Most people with foot deformities, arthritis, and diabetes benefit from customized orthotics. Also, many athletes train more safely and efficiently when they use inserts which deliver arch support and gait correction.
A Final Tip: Stretch and Warm-up Before You Workout
Wear good shoes, use customized orthotics, and prepare your feet and ankles before strenuous activities such as gym workouts, running, playing tennis or dancing. Do heel and calf stretches and other exercises your foot and ankle specialist may recommend. Also, be sure to slowly cool down after strenuous activity.
Finally, you will have a better arch support experience if you build up your tolerance for a new activity slowly. Don’t go from a sedentary lifestyle to running five miles a day. Stretch, warm up and gradually build up your strength and endurance. Your legs, ankles, feet (and particularly your heels and arches) will thank you for your sensible training schedule.
Arch Support and Other Foot and Ankle Care
At Cincinnati Foot and Ankle Care, our team of board-certified podiatrists know many treatments for a wide range of foot and ankle problems. Arch support really works to lessen or avoid pain and to preserve function.
Learn more by calling one of our 18 convenient locations for an in-depth consultation with one of our foot and ankle doctors. Or, if you wish, request a visit here. We will be in touch quickly!
Share
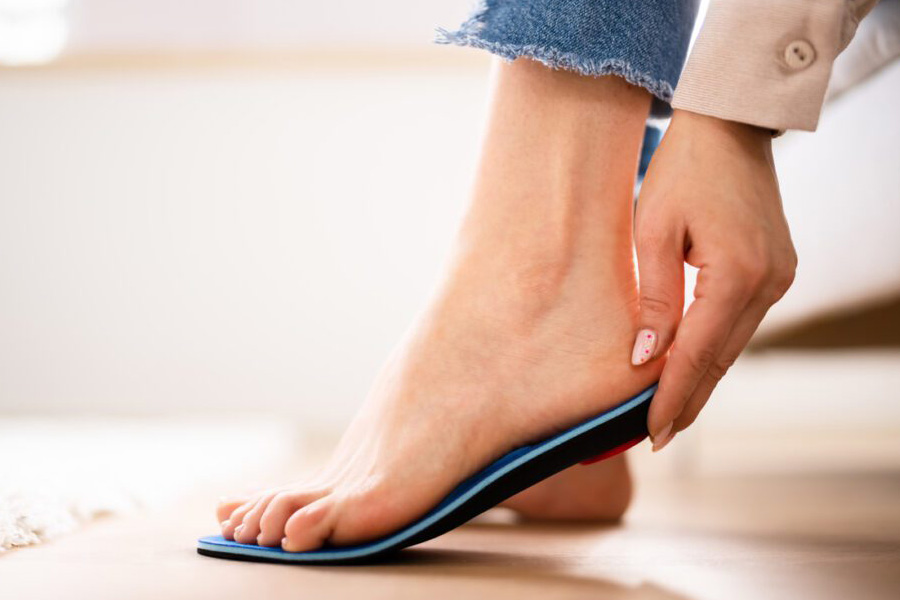
Orthotics can be very helpful in relieving pain and improving foot health.
Less pain, faster recovery, and have a lower risk of complications.


