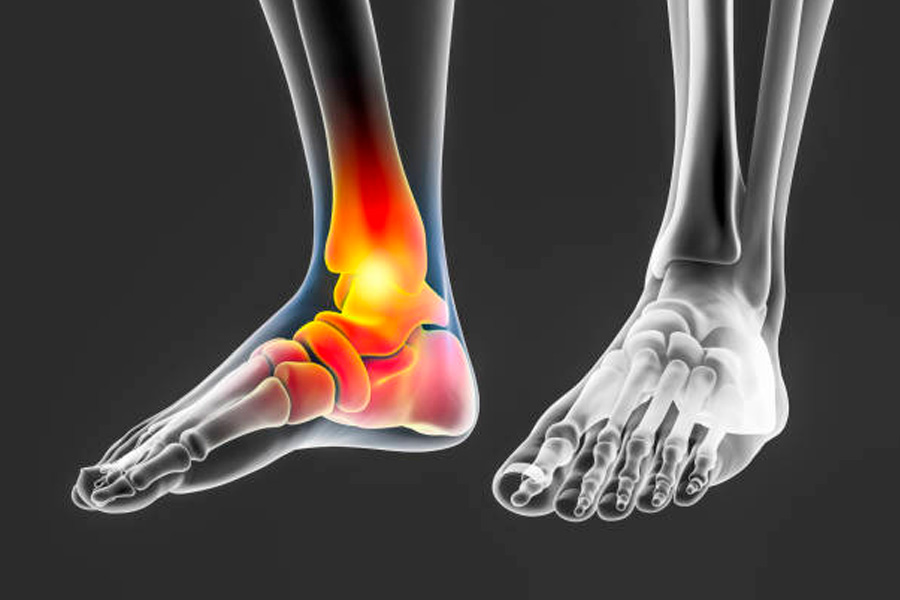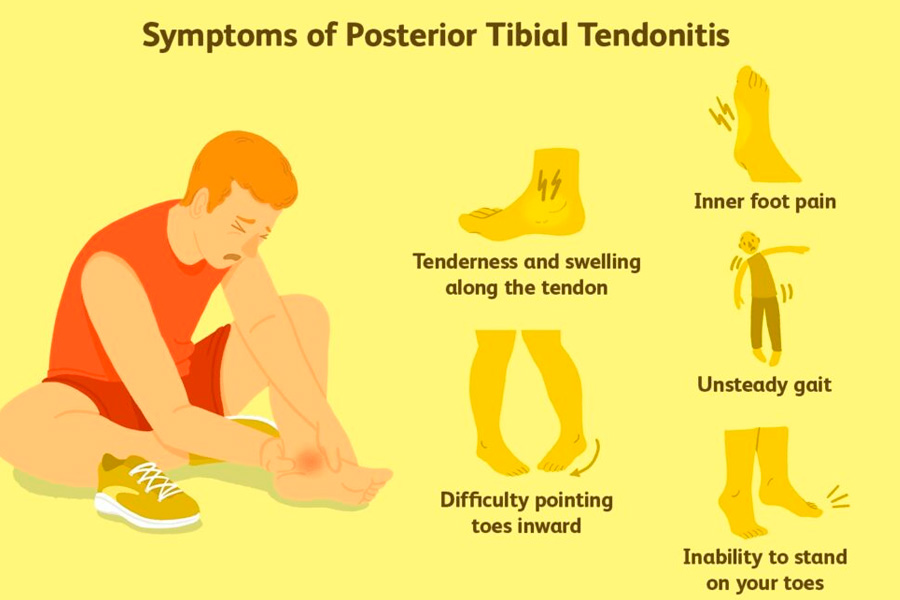
Posterior tibial tendonitis is a common foot condition that can cause significant discomfort and mobility issues. The posterior tibial tendon is crucial in supporting the arch of the foot and assisting with walking. When this tendon becomes inflamed or damaged, it can lead to pain, swelling, and a flattening of the foot’s arch.
This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of how to manage posterior tibial tendonitis symptoms effectively.
Understanding Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Before discussing the management techniques, it is essential to understand what posterior tibial tendonitis entails. This condition is often caused by tendon overuse or trauma. It is prevalent among athletes who participate in high-impact sports and individuals with flat feet or obesity due to the increased strain on the tendon.
Initial Management: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE)
One of the first strategies in managing symptoms is using the RICE method—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
This approach helps to reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain.
- Rest – Avoid activities that cause pain or discomfort, such as standing for extended periods.
- Ice – Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times per day.
- Compression – Use a compression wrap or bandage to help reduce swelling.
- Elevation – Elevate the foot above the level of the heart as often as possible to help decrease swelling.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the management of posterior tibial tendonitis. A physical therapist can provide exercises designed to strengthen the posterior tibial tendon and surrounding muscles, improving foot function and reducing pain. Additionally, balance and proprioception exercises can help improve overall foot stability.
Orthotic Devices
Orthotic devices such as custom-made shoe inserts or braces can provide much-needed support to the foot’s arch and alleviate stress on the posterior tibial tendon. An orthotic device can correct any biomechanical abnormalities contributing to tendonitis, providing long-term symptom relief.
Medication
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation associated with posterior tibial tendonitis. Your doctor may also prescribe stronger medication if your symptoms require it. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new medication regimen.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is usually considered a last resort when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. The type of surgery will depend on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health. Surgical options may include cleaning the tendon (debridement), repairing the tendon, or reconstructing the foot’s arch.
Prevention
Preventing posterior tibial tendonitis involves maintaining good foot health. You can prevent it through:
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises
- Wearing supportive footwear
- Maintaining a healthy weight
When to Visit Your Foot Doctor
While many mild cases of posterior tibial tendonitis can be managed at home using the methods described above, there are instances when it is crucial to seek professional medical help.
Persistent Pain
If pain persists despite conservative treatments such as rest, ice, compression, elevation, and over-the-counter pain relievers, it may be time to see a foot doctor. Persistent pain could indicate a more serious condition that requires a different treatment approach.
Inability to Walk or Stand
If posterior tibial tendonitis symptoms become so severe that they interfere with walking or standing, this is a clear sign to seek medical attention. Mobility issues can significantly impact your quality of life and may indicate a severe case of posterior tibial tendonitis.
Visible Deformity
Is there a visible deformity of the foot, such as a noticeable flattening of the arch or a change in the way the foot points? This is a sign that the condition may have progressed and needs professional intervention.
Non-Responsive Symptoms
If the symptoms do not improve or worsen over two weeks despite following the recommended management techniques, it is advisable to visit a foot doctor. It might be time to receive more aggressive treatment for your posterior tibial tendonitis.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis Treatment Near You in Cincinnati, OH
This type of tendinitis requires a multifaceted approach that includes rest, physical therapy, orthotic devices, medication, and potentially surgery. With the right management plan, it is possible to alleviate symptoms and improve foot function. However, prevention is always better than cure. Maintain good foot health to prevent the onset of this condition. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist despite following the management techniques described in this blog.
Looking for effective and personalized posterior tibial tendinitis treatment near you in Cincinnati? If so, look no further than Cincinnati Foot &Ankle Care (CFAC). Our highly skilled and trained podiatrists will make sure you receive the care you deserve. Contact our friendly staff at one of our 17 convenient locations across southwest Ohio if you have questions. You can also book a consultation with the best foot doctor near you by using our online appointment request form.
We look forward to helping you overcome posterior tibial tendonitis!